SHELL/Bash pre-defined variables
There are quite a few predefined variables
in BASH/Shell. These variables can be viewed by the command ‘env’ or ‘set’. Among
them, there are quite a few variables we need to understand well.
- $HOME: home directory
- $PWD: the current path
- $SHELL: The shell which you are using
- $UID: the UID
- $LOGIN: the login name for the current user
- $HOSTNAME: the hostname of the server
There are some tricky variables we need to
understand as well.
- $$: the current PID
- $#: the parameters number
- $*: all the parameters
- $!: the last run background PID
- $?: the exit code for the last command
- $_: the final argument of previous command executed.
Set variables in BASH
Usually it is suggested using all capitalized letters by convention.
To set an variable in bash, just simple use
=
eg:
go=’this’ #it will set a variable called
go, let it equals ‘this’
alternatively, you can use declare command
to set an variable.
eg:
declare go=’that’ #it
will set a variable called go, let it equals ‘that’
to use the variable, you can use $variable
name or ${variable}otherletters
eg:
echo ${go}inthemiddle
to delete the variable. You can use unset
command. But not applied for readonly variables.
eg: unset $go

Set a value to variable
There are a few ways of change the
variables.
1. read V1 V2 V3 read from standard input
2. VARIABLE=`command`
Set the variable equal to the command ‘s output.

3. Also for the BASH script we can get the parameters from the command line parameters using $1 $2 $3 etc
Variable output:
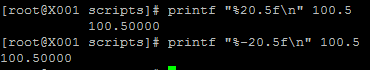
1. Simply use echo $VARIABLE to get the value2. Use printf to get the formatted value
- %s: string
- %f: float
- %d: integer
- -: left align , + : right align
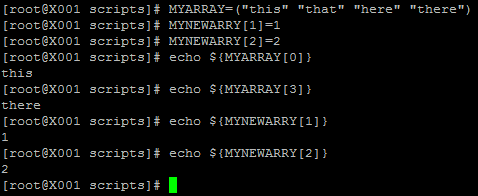
Array variables.
1.Declare an array variables:
ARRAY=(element1 element2 elment3)
Or
ARRAY[0]=element0
ARRAY[1]=element1
ARRAY[2]=element2
2. Get the value of the Array by index
${ARRAY[index]}
3. Tricky tips:
How to get the length of the array ${#ARRAY[*]}
How to copy the array: NEWARRAY=(“${ARRAY[@]}”)

No comments:
Post a Comment